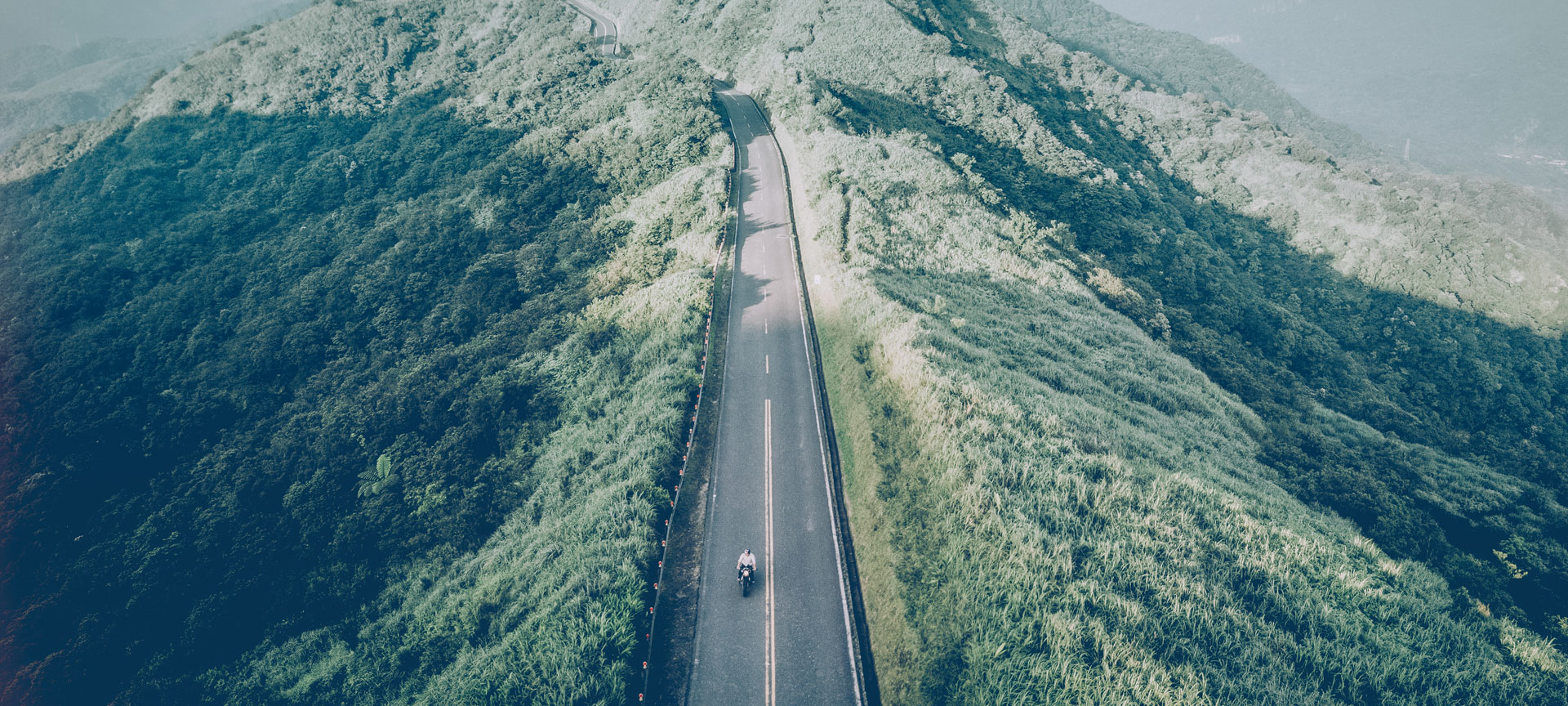
Dehesas de Sierra Morena Biosphere Reserve
A model for sustainable rural development
Right in the middle of the mountain ranges to the north of Huelva, Seville and Córdoba is the area known as Dehesas de Sierra Morena, declared a Biosphere Reserve by UNESCO in 2002. The food and livestock farming use of the area, as well as the great natural wealth it contains, have helped it earn this recognition. It’s recognised as a stargazing destination by the Starlight Foundation.
With a total area of just over 425,000 hectares, the Dehesas de Sierra Morena are the largest of the Spanish network of biosphere reserves. Its territory, as well as including a further 8,000 hectares of unprotected areas, includes three natural parks in the north of Andalusia: Sierra de Hornachuelos, in Cordoba; Sierra Norte, in Seville; and Sierra de Aracena y Picos de Aroche, in Huelva. The Sierra de Hornachuelos provides the reserve with a Mediterranean mid-mountain ecosystem with varied flora and fauna, although both are richer in the Vega del Guadalquivir. Chestnut tree forests flood the landscape of the Sierra de Aracena and Picos de Aroche, north of the province of Huelva; and in the Seville sector, in the heart of the Sierra Norte, holm oak forests dominate and, in the wettest areas, gall oaks sprout up. However, the most representative and common feature of the reserve is undoubtedly the dehesa. This natural Mediterranean scenery, made up of extensive pastures populated by holm oaks and cork oaks, has been the basis of the area's economy for centuries, due to the agricultural and livestock use of this space. Precisely, the uniqueness of the dehesa within the global agricultural context has been one of the factors that has led UNESCO to declare this area a biosphere reserve, as it embodies a model of sustainable development, allowing human development without any harm to the conservation of its great biodiversity.
Dehesas de Sierra Morena Biosphere Reserve
Andalusia
Cordoba (Andalusia):
- -
- -
- -
Huelva (Andalusia):
Seville (Andalusia):
Activa JS
What you need to know
-
Cultural information
The area's inhabitants have managed to exploit the main natural resources of the reserve through various activities, such as the extraction of cork from the cork oaks, hunting and the herding of fighting bulls and Iberian pigs. A total of 43 municipalities belonging to the three Andalusian provinces make up this area, including picturesque mountain villages such as Hornachuelos, Aracena, Jabugo or Cazalla de la Sierra.
-
Environmental information
The Dehesas de Sierra Morena are home to a wide range of plant species, with a predominance of holm oaks, cork oaks and various typically Mediterranean shrub species. Numerous species representative of the Mediterranean fauna coexist in this area, such as the Iberian lynx, the wolf, the black stork, the otter, the genet and the dormouse. It is also worth mentioning the abundant presence of birds of prey: black vulture, imperial eagle and short-toed eagle, sparrowhawk, and peregrine falcon, etc.
-
Information for visits
The reserve can be accessed through any of the three natural parks that make up the reserve: Sierra de Aracena and Picos de Aroche, Sierra Norte, Seville and Sierra de Hornachuelos. There are information offices in Aracena (Huelva), Constantina (Seville) and Hornachuelos (Visitors' Centre “Huerta del Rey”).
Travel plans for inspiring you



